My Work on the NVIDIA TAO Toolkit 4.0: People Re-Identification and Pose-Based Action Recognition Networks
Published:
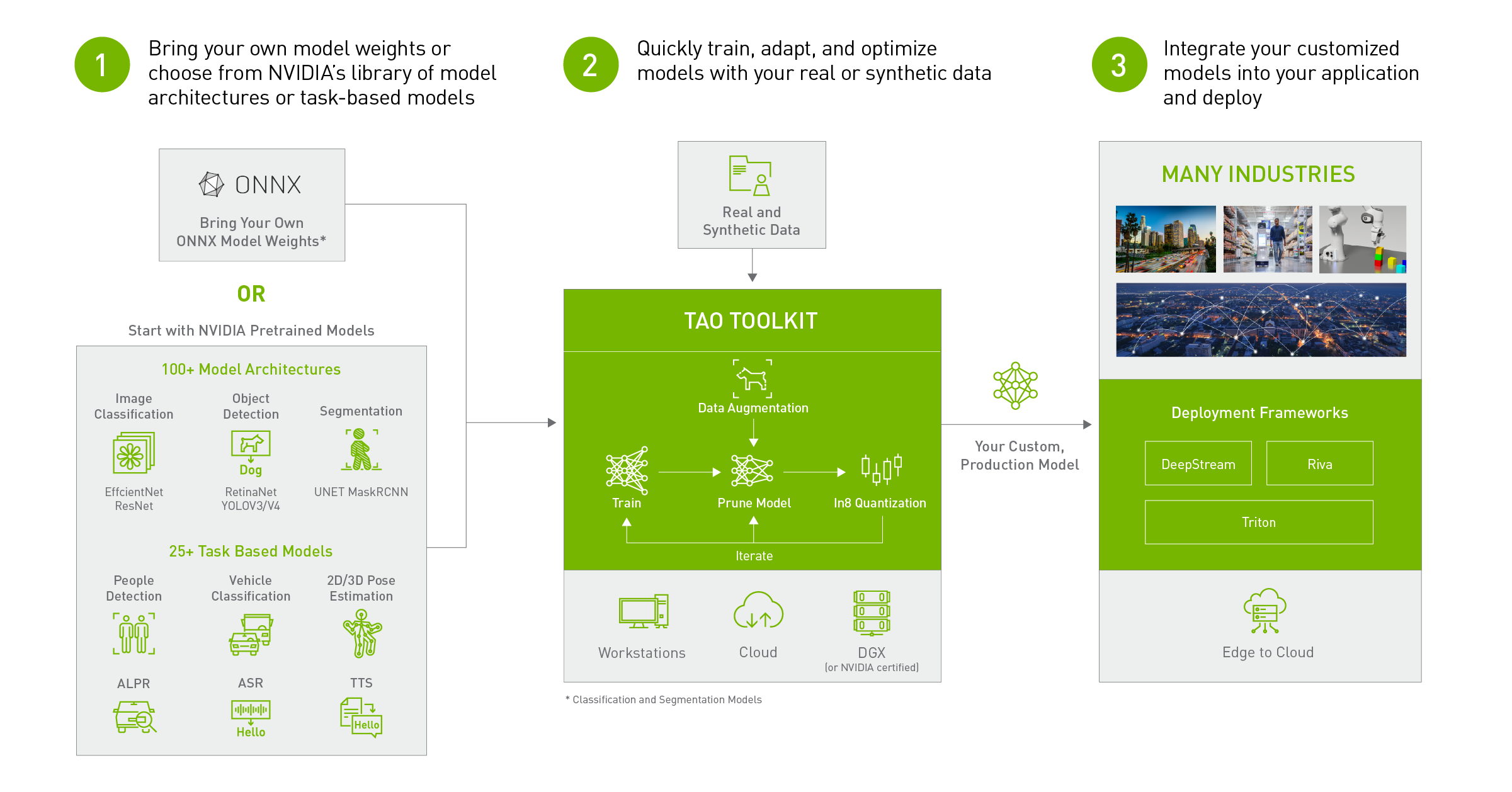
NVIDIA has recently announced the release of the TAO Toolkit 4.0, which includes several exciting new features and enhancements. As a developer who has contributed to the toolkit, I’m thrilled to share my experience working on the people re-identification and pose-based action recognition networks, as well as the end-to-end video analytics pipelines on the Triton Inference Server.
At its core, the TAO Toolkit simplifies the process of creating AI models, making it easier for developers to get started and boost productivity. My contribution to the toolkit includes the development of the people re-identification and pose-based action recognition networks. People re-identification is the process of matching people across different cameras in a video surveillance system, while pose-based action recognition identifies and classifies human actions based on their body poses. To showcase the capabilities of these networks, I provided end-to-end inference samples on the Triton Inference Server, which is an open-source inference serving software that standardizes model deployment and execution, delivering fast and scalable AI in production. These Triton samples consume TensorRT engines and support running with various sources. The exported models from TAO can be directly deployed in the Triton apps, making it easy to get started with AI model deployment.
The latest version of TAO Toolkit 4.0 includes several exciting new features that enhance the developer experience, including source code availability with the Enterprise license, turnkey deployment of TAO into various cloud services, integration with third-party MLOps services, TAO on Google Colab, new Transformer-based vision models, and support for newer GPUs such as H100, L40, and L4.
One of the standout features of TAO Toolkit 4.0 is its ability to automatically fine-tune hyperparameters with AutoML. This feature saves developers valuable time and effort by automating the process of fine-tuning hyperparameters, making it easier to create accurate and efficient models. With turnkey deployment of TAO into various cloud services, including Azure ML, Google Vertex AI, Azure Kubernetes Services (AKS), and Amazon EKS, developers can quickly deploy their models to the cloud and scale as needed.
Finally, TAO Toolkit 4.0 now includes complete access to TAO source code and model weights for the pretrained models without encryption using NVIDIA AI Enterprise software suite. This feature provides developers with greater flexibility and control over their AI models, allowing them to customize and adapt models to their specific needs.
Overall, my experience working on the NVIDIA TAO Toolkit 4.0 has been incredibly rewarding. I’m excited to see how the toolkit continues to evolve and empower developers to create innovative and impactful AI solutions.